Wastewater Treatment
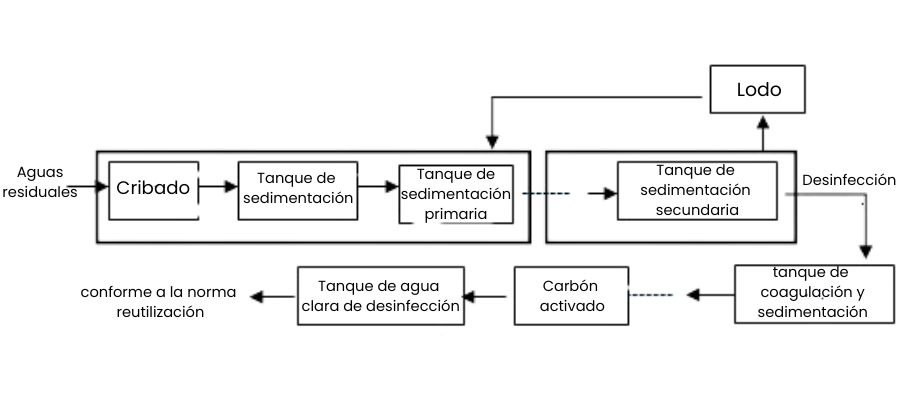
The pretreatment phase of the wastewater treatment process begins with collection, screening and water quality adjustment. Domestic, industrial and other wastewater is collected through pipes, screened and sand settling tanks are used to remove impurities in the form of large particles, and pH and suspended solids concentrations are adjusted to ensure that the wastewater is suitable for further treatment.
This is followed by the primary and secondary treatment stages. In primary treatment, wastewater undergoes sedimentation, flotation and activated sludge to remove suspended solids and convert organic matter to inorganic matter. Secondary treatment further degrades organic matter through aerobic treatment and aerobic digestion, and finally removes microorganisms and sludge in a settling tank. Finally, tertiary treatment removes residual organic contaminants and heavy metals through filtration, activated carbon adsorption and disinfection to ensure that the treated water is safe for use.
Activated Carbon For Wastewater Treatment

Granular Activated Carbon
| Raw Materials | coal |
| Iodine Value | 600-1050mg/g |
| Size | 8-30mesh、12-40mesh |
| Hardness | ≥95% |
Powdered Activated Charcoal
Carbon-based powdered activated carbon is commonly used in wastewater treatment. It has a large specific surface area and rich microporous structure, which enables it to effectively adsorb a wide variety of organic pollutants, heavy metal ions and other difficult-to-biodegrade substances in wastewater. It is used for batch adsorption, in which the powdered carbon is added to the water to be treated, thoroughly mixed and separated by sedimentation or filtration. This method is also known as static adsorption.
The parameters are as follows:
| Iodine Value | 700-1050mg/g |
| Size | 200mesh、325mesh |
| Ash | ≤9% |
