Biogas is an important source of renewable energy. However, the biogas production process often contains H₂S. Hydrogen sulfide is a highly corrosive and toxic compound that not only causes serious damage to equipment, but also poses a threat to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is important to remove hydrogen sulfide from biogas before it can be used.
In this article, we will detail the key role of activated carbon in removing hydrogen sulfide from biogas, discuss how it works and how to select the right type of activated carbon. If you are looking for an effective solution for biogas treatment, this article will provide you with a complete guide.
Why is it necessary to remove hydrogen sulfide from biogas?

Hydrogen sulfide is one of the most important contaminants in biogas, which is generated when sulfur-containing organic compounds decompose anaerobically. The presence of H₂S in biogas causes the following problems:
- Equipment corrosion: H₂S is highly corrosive and can severely damage piping, motors and other metal parts of the biogas system, reducing the life of the equipment.
- Health risks: H₂S is toxic to humans and animals at high concentrations, and can even be fatal.
- Environmental contamination: The combustion of biogas containing H₂S generates sulfur dioxide (SO₂), which is one of the main causes of acid rain.
- Reduction of energy value: The presence of H₂S affects the combustion efficiency of biogas, which reduces its energy value.
Therefore, removing hydrogen sulfide during biogas production and use is a crucial step.
How does activated carbon remove hydrogen sulfide?
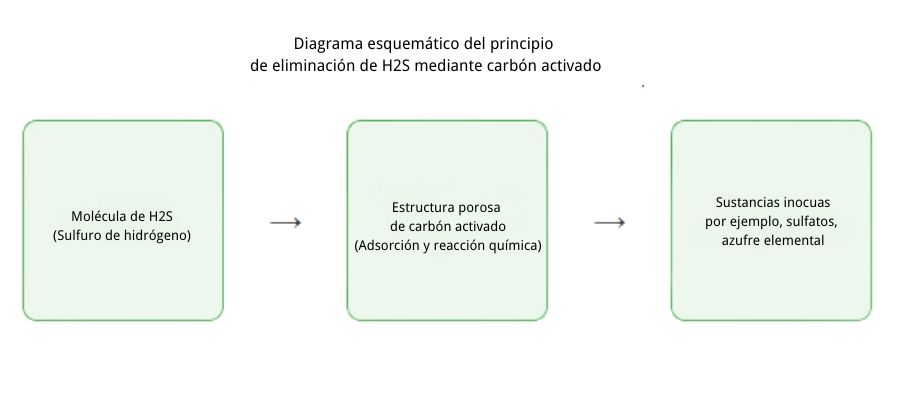
Activated carbon is a porous material with extremely high adsorption capacity, making it an ideal choice for removing contaminants such as hydrogen sulfide. Through the following principles, activated carbon can effectively remove H₂S from biogas:
- Chemical adsorption: H₂S molecules adsorb on the surface of the activated carbon and react with chemical groups on its surface, forming sulfur or other inert compounds.
- Catalytic oxidation: Activated carbon impregnated with chemical agents (such as metal oxides) can catalyze the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide, converting it into sulfur or harmless sulfur salts.
Advantages of using activated carbon to remove H₂S:
- High adsorption capacity: Activated carbon has a large surface area and a developed porous structure, which enables it to adsorb a large amount of H₂S molecules and ensure their total removal.
- Great adaptability: Activated carbon maintains its adsorption efficiency over a wide range of temperature and humidity conditions, making it suitable for the removal of H₂S in biogas, natural gas and industrial gases.
- No secondary contamination: During adsorption of H₂S, activated carbon does not generate secondary pollution, preventing the emission of harmful waste liquids or gases.
- Flexibility and customization: We offer a variety of types of activated carbon for H₂S removal, which can be chosen according to the specific needs of each application and adapted to different industrial environments.
Types of activated carbon for hydrogen sulfide removal
The choice of the appropriate type of activated carbon depends on the hydrogen sulfide concentration, biogas flow rate and operating conditions. Some common types of activated carbon and their characteristics are described below:
Activated carbon impregnated with KI

Activated carbon impregnated with KI is a highly efficient material for the removal of hydrogen sulfide, which has a higher chemical reaction capacity due to the impregnation with potassium iodide.
Principle of operation:
Activated carbon impregnated with potassium iodide can catalyze the oxidation of H₂S, converting it to elemental sulfur (S).
Reaction equations:
- H₂S + ½ O₂ → S + H₂O
- 2 CH₃-CH₂-SH + ½ O₂ → CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-SS-CH₂-CH₂-CH₃ + H₂O
Features and benefits:
- Suitable for low humidity and high hydrogen sulfide concentration environments.
- High H₂S removal efficiency, especially in high concentration applications.
- It does not produce pollutant by-products during H₂S removal.
Activated carbon impregnated with NaOH

NaOH-impregnated activated carbon is a strong alkaline activated carbon, mainly used to neutralize and adsorb acid gases.
Principle of operation:
NaOH-impregnated activated carbon has alkali groups on its surface that react with hydrogen sulfide, generating sodium sulfide (Na₂S) or sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS). Reaction equation:
H₂S + 2NaOH → Na₂S + 2H₂O
Features and benefits:
- Quickly and efficiently removes acid gases, especially H₂S.
- It is not sensitive to humidity, maintaining its efficiency even in high humidity conditions.
- Easy to operate, suitable for continuous flow gas treatment systems.
Activated carbon impregnated with KOH

KOH-impregnated activated carbon is similar to NaOH-impregnated activated carbon, but with superior performance, especially in high humidity conditions.
Principle of operation:
KOH is a strong alkali that reacts with H₂S, forming potassium sulfide (K₂S). KOH has a higher chemical activity than NaOH, allowing H₂S to be removed in less time. Reaction equation:
H₂S + 2KOH → K₂S + 2H₂O
Features and benefits:
- High efficiency: It shows excellent performance under conditions of high humidity and high H₂S concentration.
- Long service life: KOH-impregnated activated carbon has a longer saturation time, which reduces the frequency of replacement.
- Broad applicability: In addition to removing H₂S, it can also remove other acidic contaminants.
Catalytic activated carbon

Catalytic activated carbon is modified on its surface with the addition of catalysts (such as metal oxides), which allows catalyzing the hydrogen sulfide oxidation reaction. This type of activated carbon is one of the most efficient materials for the removal of H₂S.
Principle of operation:
Catalysts on the surface of the activated carbon facilitate the oxidation of H₂S to elemental sulfur or sulfur salts without the addition of additional oxidants.
Basic reaction equation:
H₂S + O₂ (from the air) → S + H₂O
Advantages:
- It does not require additional chemical additives, which makes it more environmentally friendly.
- By-products, such as elemental sulfur, can be recycled.
Conclusion
Removing hydrogen sulfide from biogas is crucial to improve the value of biogas, protect equipment and reduce environmental pollution. By choosing the right type of activated carbon, you can significantly improve desulfurization efficiency and reduce operating costs.
PuroCarbon S.L. offers a wide range of high efficiency activated carbon products that can meet various biogas treatment needs. If you need further technical support or would like to know more about our products, please do not hesitate to contact us. contact with us.
